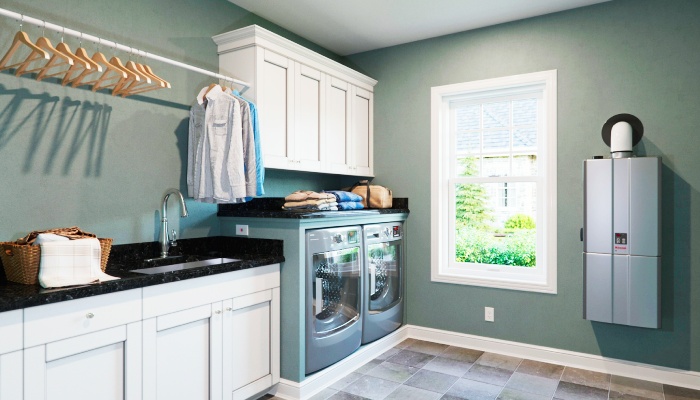
In the quest for more sustainable lifestyles, homeowners and builders alike are increasingly turning towards innovative technologies that not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance living standards. Among these innovations, tankless electric water heaters, also known as instantaneous water heaters, emerge as a key component in the sustainable home design paradigm. Unlike traditional water heaters that constantly heat and reheat water in a large tank requiring energy to store hot water even when not in use tankless models provide continuous hot water on demand, offering a more energy-efficient solution.
This introductory section delves into the concept of sustainable home design and the pivotal role of tankless electric water heaters within it, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of how these devices contribute to eco-friendly living. The benefits of tankless hot water heaters, including reduced energy consumption, elimination of the need to store hot water, and the provision of instant hot water, underscore their value in sustainable home design. By understanding the significance of energy efficiency and the advantages of adopting such technologies, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with the principles of sustainability and conservation.
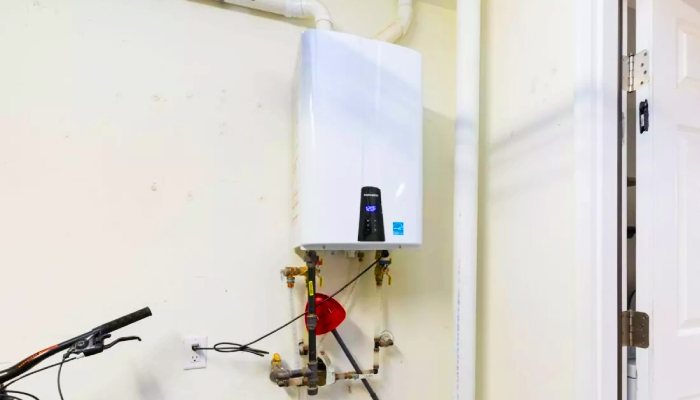

Understanding Tankless Electric Water Heaters
2.1 Technology Behind Tankless Electric Water Heaters
Tankless electric water heaters, particularly popular in regions like Australia, represent a significant advancement in residential hot water systems. Known also as on-demand or instant water heaters, these devices eliminate the need for storing large volumes of hot water, instead heating water directly as it flows through the unit. This process begins when a hot water tap is activated, prompting cold water to travel through a pipe into the heater where electric heating elements can warm it to the required temperature instantaneously. This on-demand heating mechanism is a departure from traditional methods that continuously heat and reheat water in a storage tank, leading to energy losses. The efficiency and immediate hot water delivery of tankless systems highlight their role in promoting more sustainable and energy-conscious home environments.
2.2 Advantages of Tankless Systems
The transition to tankless electric water heaters, including those used in Australia, is motivated by their multiple benefits over conventional tank-based systems. Their foremost advantage is energy efficiency. By eliminating the need on demand water heater to constantly maintain a reservoir supply of hot water throughout, these heaters can drastically cut down on energy use and, by extension, utility expenses. This efficiency is a crucial factor for Australian homes, where energy conservation and cost savings are significant concerns.
Moreover, tankless heaters are celebrated for their longevity, often outlasting traditional water heaters by several years. This durability means less frequent need for replacements, contributing to both the environmental benefits of conservation and financial savings over the tankless heater’s lifespan.
The compact design of tankless water heaters is another plus, allowing them to be mounted on a wall and freeing up floor space a feature that is especially valuable in smaller living spaces common in many Australian cities.
Additionally, the ability of tankless electric element heaters to provide an uninterrupted and continuous hot water supply also ensures that households never experience the discomfort of running out of hot water, especially during times of high demand. This reliability, alongside the system’s efficiency and space-saving design, positions tankless electric water heaters as a preferred choice for enhancing the sustainability and comfort of Australian homes.
The shift towards these innovative heating solutions reflects a broader move towards sustainable living practices. By installing energy efficient appliances and choosing tankless electric water heaters, homeowners not only embrace energy efficiency and utility savings but also contribute to the overarching goal of reducing environmental impact, marking a forward leap in sustainable home design.

Environmental Impact
3.1 Energy Savings and Efficiency
Tankless electric water heaters represent a significant leap forward in home energy efficiency. Unlike traditional water heaters that continuously heat and reheat water to maintain a preset temperature, tankless models heat water on demand. This distinction means that energy consumption only occurs during actual use, eliminating standby heat loss and energy losses associated with tank storage models. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that tankless water heaters can be 24% to 34% more energy efficient for homes that use 41 gallons or less of hot water daily. For households with a higher demand, efficiency gains from tankless units can still be 8% to 14%. When installed at each hot water outlet, their efficiency can skyrocket, offering energy savings that are both immediate and impactful over the long term.
3.2 Reduced Carbon Footprint
By significantly reducing energy consumption, tankless electric water heaters play a crucial role in decreasing a household’s carbon footprint. The superior energy efficiency of tankless systems translates directly into lower greenhouse gas emissions, as less energy used means less energy produced and fewer emissions from power plants. This is especially true in regions where electricity comes from renewable sources. Furthermore, because these systems are more durable than traditional water heaters, with a life expectancy of more than 20 years (compared to 10-15 years for traditional heaters), they contribute to reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements traditional tank heaters. The reduced carbon footprint and minimized environmental impact of tankless water heaters align with the goals of sustainable living, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious homeowners.
3.3 Sustainability Benefits
Adopting tankless electric water heaters contributes to broader sustainability benefits beyond just energy savings and carbon footprint reduction. These systems demand less raw material for manufacturing and, due to their longer lifespan, result in less waste and fewer demands on landfill. Additionally, their compact size reduces the spatial footprint, offering more flexibility in home design and potentially reducing the materials needed for housing infrastructure. The shift towards electric tankless water heaters is a reflection of a larger trend in sustainable home design: choosing appliances and systems that not only reduce operational costs and environmental impact but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient use of resources.
Economic Considerations
4.1 Cost Analysis
While the initial cost of a tankless electric water heater is typically higher than that of a traditional tank model, the long-term savings can be substantial. The energy efficiency of tankless heaters means lower monthly utility bills, with savings that can offset the higher upfront cost over time. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that homeowners can save hundreds of dollars annually on their energy bills by switching to electric tankless water heater models. Furthermore, the longer lifespan of tankless heaters means they need to be replaced less often, contributing to cost savings over time. When considering the total cost of ownership, including purchase, installation, operation, and maintenance, tankless electric water heaters can be more economical than traditional tank heater models.
4.2 Incentives and Rebates
To encourage the adoption of energy-efficient appliances, many governments and utilities offer incentives and rebates for tankless electric water heaters. These can significantly lower the initial investment of storage tank heaters, making them a more attractive option for homeowners. Rebates can vary by location and provider but often cover a significant portion of the purchase and installation costs. Additionally, some tankless models qualify for federal tax credits for energy efficiency, providing further financial savings. Homeowners are encouraged to research local and federal incentives as part of their purchasing decision. These economic incentives, combined with the long-term energy savings, make tankless electric water heaters an economically viable and attractive option for many households, aligning financial savings with environmental sustainability.
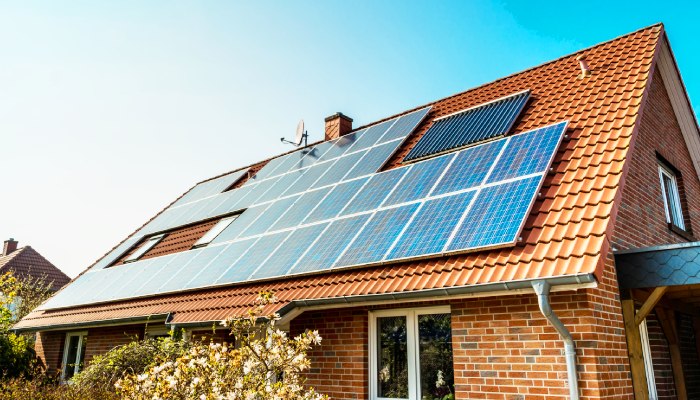

Implementation in Sustainable Home Design
5.1 Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The compatibility of tankless electric water heaters with renewable energy sources significantly enhances their role in sustainable home design. These systems can be efficiently powered by solar panels or wind turbines, further reducing the environmental impact and operational costs. By leveraging renewable energy, homeowners can achieve near-zero energy consumption for water heating. This integration aligns with the principles of sustainable design, which prioritize the use of clean energy sources to minimize reliance on fossil fuels. Moreover, the flexibility and compact size of tankless storage water heaters allow for easier integration into homes designed with a focus on energy efficiency and minimal environmental footprint. As renewable technologies become more accessible and affordable, the synergy between tankless water heating systems and renewable energy sources is expected to play a pivotal role in the evolution of sustainable homes.
5.2 Smart Home Compatibility
Tankless electric water heaters fit seamlessly into the smart home ecosystem, enhancing energy efficiency through intelligent management. Equipped with advanced technology, these heaters can be integrated with home automation systems to optimize hot water supply based on actual usage patterns and preferences. This capability allows for dynamic adjustments endless hot water supply, such as lowering the temperature during periods of low demand or when the household is away, leading to additional energy savings. The integration with smart thermostats and energy management systems provides homeowners with real-time insights into their hot water demand and heating consumption, enabling more informed decisions about energy use. This level of control and efficiency is a cornerstone of sustainable home design, where every component works in harmony to reduce waste and increase sustainability.
5.3 Case Studies
Exploring successful implementations of tankless electric water heaters in sustainable homes provides valuable insights into their benefits. One case study involves a zero-energy home that utilizes solar panels to power a tankless water heater, achieving a net-zero energy balance for hot water usage. Another example is a renovation project where a full tankless water heater system was integrated with a smart home system, resulting in a 30% reduction in energy consumption for water heating. These case studies demonstrate the practicality and effectiveness of tankless heaters how much hot water, in diverse settings, from new constructions focused on sustainability to retrofitting existing homes for energy efficiency. By showcasing real-world applications, these examples highlight the versatility and adaptability of tankless electric water heaters in achieving sustainable living goals.
Challenges and Solutions
6.1 Addressing High Initial Costs
The higher initial cost of tankless electric water heaters compared to traditional models is a significant barrier for some homeowners. However, this challenge can be mitigated through a variety of strategies. Researching and taking advantage of available rebates and tax incentives can substantially reduce upfront costs. Financing options, such as low-interest loans for energy-efficient home improvements, can also make the investment more manageable. Homeowners should consider the long-term savings on energy bills, which can offset the initial investment over time. Educating consumers about the total cost of ownership, including the extended lifespan and lower operating costs of tankless heaters over traditional tank systems, can help them make informed decisions.
6.2 Overcoming Installation Challenges
Installation challenges, including the need for electrical system upgrades and space considerations, can deter homeowners from choosing tankless electric water heaters. To address these issues, it’s essential to consult with qualified professionals who can assess the home’s electrical capacity and recommend necessary upgrades. The compact design of tankless models offers flexibility in placement, allowing for installation in smaller or unconventional spaces. For retrofitting projects, exploring different, tankless heater models and configurations can identify solutions that minimize the need for extensive modifications. By providing clear information on installation requirements and potential challenges, professional installation, along with professional guidance and support, homeowners can navigate these obstacles more effectively, making the transition to a tankless system smoother and more accessible.
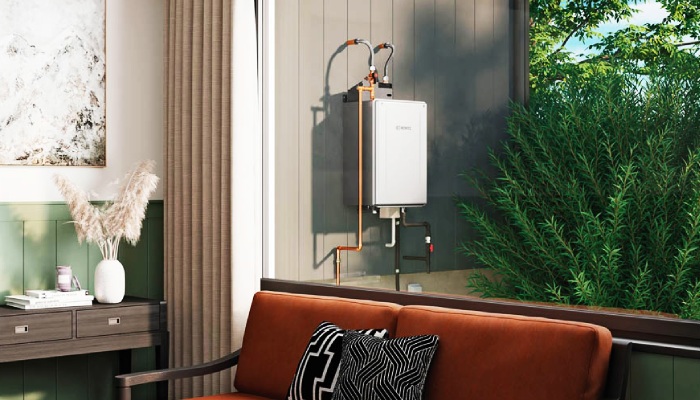

Future Trends in Tankless Water Heating Technology
As we look towards the future, tankless electric water heating technology is set to evolve further, integrating more seamlessly with renewable energy sources, smart home technologies, and innovative materials to enhance efficiency and user experience. Innovations in this space are likely to focus on increasing energy efficiency, reducing installation costs, and enhancing durability. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) will enable smarter, more adaptive water heating solutions that can learn from usage patterns and adjust heating schedules and temperatures for optimal efficiency and comfort. Future models on demand hot water front may also feature advanced diagnostics and maintenance alerts, making it easier for homeowners to maintain and service their systems.
Additionally, the push towards greener, more sustainable energy sources is expected to drive the adoption of tankless water heaters compatible with solar and wind energy. This compatibility will further reduce the energy factor and the carbon footprint of residential water heating and align with global sustainability goals. As materials science advances, we can also expect to see the development of more compact and efficient heaters, using less energy to achieve the same level of water heating.
Conclusion
The role and benefits of tankless electric water heaters in sustainable home design are increasingly significant, offering a practical solution to reduce energy consumption, lower carbon emissions, and enhance overall efficiency. Their benefits, including immediate access to hot water, energy savings, reduced environmental impact, and economic advantages, underscore the importance of these systems. Tankless models, also known as instantaneous water heaters, eliminate the need to continuously store hot water, significantly reducing energy wastage and offering a more efficient way to heat water only as needed. This capability not only leads to substantial energy savings but also contributes to a much smaller environmental footprint, aligning perfectly with the goals of sustainable living.
Despite the challenges associated with higher initial costs and installation, the long-term savings, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, coupled with the potential for integration with renewable energy sources and smart home technologies, present a compelling case for their adoption. The benefits of tankless water heating, such as reduced energy and water usage, play a crucial role in sustainable home design, offering an attractive option for homeowners looking to enhance the sustainability of their homes.
As we move forward, the continued innovation in tankless water heating technology, along with growing awareness of environmental sustainability and energy costs, is likely to increase their prevalence in homes around the world. Homeowners, builders, and designers are encouraged to consider the benefits of tankless water heaters as a key component of sustainable home design, contributing to a greener future. By embracing these technologies, individuals can play a part in the global effort to reduce energy consumption and combat climate change, making a positive impact for generations to come.