Hot water systems are an essential component of both residential and commercial infrastructure, providing the necessary comfort and functionality for daily activities such as bathing, cooking, and cleaning. The choice of a hot water system is a significant decision influenced by various factors including cost, efficiency, and space considerations. However, an often overlooked yet critical aspect of new hot water system is the longevity and life expectancy of these systems. Understanding how long a hot water system is likely to last, and what impacts its durability, can help homeowners and building managers make informed decisions that ensure both economic and environmental efficiency.
We will explore the longevity and life expectancy of various types of hot water systems, including conventional water tank and storage heaters, tankless systems, heat pump water heaters, and solar-powered models. We will delve into how these systems operate, discuss the factors that affect their lifespan, and provide insights into how maintenance can extend their functionality. By the end of this exploration, readers will be equipped with the knowledge needed to choose and maintain a hot water system that aligns with their needs and expectations for performance and longevity.
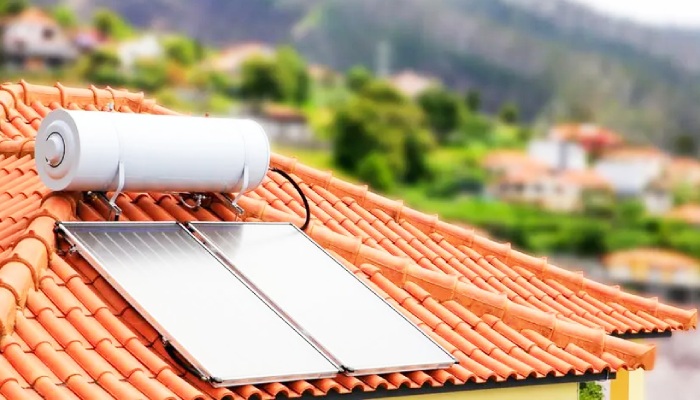

Overview of Hot Water Systems
When considering hot water system types, there are several popular options each with its own set of advantages and operational dynamics. Understanding the different, electric hot water systems have can aid in selecting the right one for specific needs based on factors such as energy source, efficiency, cost, and installation requirements.
- Tank Storage Heaters: These are the most traditional form of water heating systems. Tank heaters operate by storing a set amount of water and keeping it heated to a preset temperature. The water is heated via gas burners or electric elements. While generally less efficient due to standby heat loss, they are popular due to their lower initial cost and straightforward installation.
- Tankless Water Heaters: Also known as on-demand water heaters, these systems heat water directly without the use of a storage tank. When a hot water tap is turned on, cold water travels through a pipe into the unit where it is heated by either gas or electricity. Tankless water heaters are more energy-efficient than traditional tank heaters because they eliminate the need to continuously heat a tank full of water.
- Heat Pump Water Heaters: These systems use electricity to move heat from one place to another instead of generating heat directly. Essentially, they operate like a refrigerator in reverse. Heat pump water heaters are significantly more energy-efficient than conventional electric water heaters and work best in moderate climates.
- Solar Water Heaters: Utilizing solar panels typically installed on the roof, these systems capture and convert sunlight into heat energy, which is then transferred to water in a storage tank. Solar water heaters can significantly reduce energy costs, but their effectiveness is dependent on geographic location and weather conditions.
Each of these systems has its unique characteristics and benefits. By understanding the fundamental workings and advantages of each, consumers can make a more informed decision tailored to their specific hot water heater needs.
Factors Affecting Longevity
The durability and functional lifespan of hot water systems are influenced by a variety of factors. Understanding these can help extend the life of the hot water system last, and optimize its performance over time.
Water Quality
Hard water, which is high in mineral content, can lead to scale accumulation in water heaters. This build-up can reduce efficiency of heat pump hot water and increase the strain on the system, potentially leading to premature failure.
Usage Patterns
Frequent on and off cycling of a hot water system can cause wear and tear on components, particularly in tankless systems. High demand for hot water increases the operational load and can shorten the lifespan of the electric hot water system.
Maintenance Frequency
Regular maintenance of hot water tank, such as flushing the tank to remove sediment, checking the anode rod, and inspecting the system for leaks and corrosion, is crucial in extending the life expectancy of hot water systems.
Installation Quality
Proper installation affects the efficiency and longevity of hot water systems. Incorrect installation can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased wear and tear, and ultimately, a reduced lifespan gas hot water system.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as the climate and placement of the unit (e.g., in a basement vs. an outdoor setting) can also impact the longevity. External conditions like temperature extremes can influence the performance and durability of the system’s lifespan.
By addressing these factors, homeowners can significantly improve hot water systems last and the longevity and efficiency of their hot water systems, ensuring reliable hot water supply and minimizing the need for premature replacements.
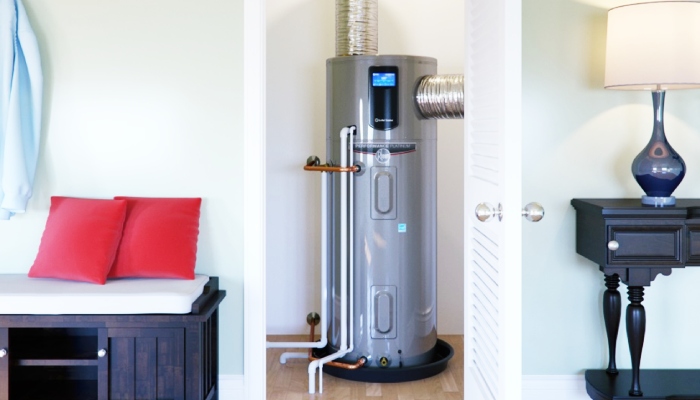

Comparative Analysis of System Longevity
Different hot water systems offer varying lifespans, which can influence a homeowner’s choice long do hot water, depending on their long-term cost implications and maintenance needs.
Tank Storage Heaters
Typically, these systems have a lifespan of about 8-12 years. Their longevity can be affected by factors such as the quality of gas hot water, and the frequency of maintenance.
Tankless Water Heaters
These units can last up to 20 years or more, nearly double the average lifespan of tank storage heaters. Their longevity is due in part to fewer corrosion risks since water is not stored for long periods.
Heat Pump Water Heaters
With proper maintenance, heat pump electric systems often can operate efficiently for about 10-15 years. They tend to have longer lifespans than traditional electric or gas heaters due to their less intensive heating process.
Solar Water Heaters
These systems can have the longest lifespan, often lasting 20 years or more. The longevity is significantly influenced by external factors like exposure to harsh weather conditions, which can affect the solar collectors.
This analysis shows that while the initial cost and installation complexity of a hot water heater for some systems like solar and tankless heaters may be higher, their extended lifespans provide long-term savings and reduced environmental impact. Homeowners should consider these factors in the context of their specific needs and local conditions when selecting a hot water system.

Maintenance Tips for Extending Life Expectancy
Proper maintenance is key to maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of water unit in any hot water system. Here are specific tips for each type of system to help ensure they operate effectively for as long as possible:
- Tank Storage Heaters:
- Annual Inspections: Check for rust, leaks, and other signs of wear. Replace the anode rod every 3 to 5 years to prevent corrosion inside the tank.
- Regular Flushing: Drain the tank at least once a year to remove sediment that can build up and cause inefficiency or damage.
- Tankless Water Heaters:
- Flush System Annually: Use a vinegar solution to flush out scale and mineral build-up that can affect heating efficiency.
- Clean Air Intake Filters: Regular cleaning or replacement of filters will prevent obstructions that can reduce performance.
- Heat Pump Water Heaters:
- Clean the Air Filters and Coils: Ensure these are free of dust and debris to maintain optimal efficiency.
- Check the Condensate Drain: Ensure it is not clogged to prevent water damage and maintain operational efficiency.
- Solar Water Heaters:
- Check for Scale: Solar thermal systems need regular checks for scale in solar collectors and pipes.
- Inspect Solar Panels and Piping: Regularly check for any physical damage or leaks and ensure that the solar panels are clean and unobstructed.
Following these maintenance steps can significantly extend the life of hot water systems, enhance their performance, and lead to substantial savings in energy and repair costs.

Economic and Environmental Impact of Hot Water System Choices
When selecting a hot water system, the economic and environmental impacts are crucial considerations that go hand-in-hand with understanding the longevity and life expectancy of different hot water systems. This section explores how gas and electric systems compare to more sustainable options like solar hot water systems, considering their costs, energy usage, and environmental footprints.
Gas and Electric Systems
Traditional water heater systems, both gas and electric, are widely used due to their ability to provide hot water on demand. However, while these systems are initially less costly, their operational costs over time can add up due to energy consumption and maintenance needs. Gas systems generally have lower operational costs compared to electric systems but may have a greater environmental impact due to carbon emissions.
Hot Water System Lifespan
The lifespan of traditional hot water heaters typically ranges from 8 to 12 years for tank models and up to 20 years for tankless models. The longevity of these systems is a significant factor in their overall cost-effectiveness. Frequent replacements and the need for more frequent maintenance can negate the initial savings from cheaper models.
Solar Hot Water System
Solar hot water systems represent a more sustainable investment. While the initial installation cost is higher, the long-term savings are substantial due to the reduction in energy costs. Solar systems can also have lifespans exceeding 20 years, making them more appealing when considering how much hot water a household requires over time. Additionally, they have a minimal environmental impact as they utilize renewable energy, reducing the carbon footprint associated with heating water.
Environmental Considerations
The choice between gas, electric, and solar hot water systems also reflects a homeowner’s environmental commitment. Electric systems, while typically using more energy, can be powered by renewable sources depending on the grid’s energy mix, thus potentially reducing environmental impact. Gas systems, despite their efficiency, still rely on fossil fuels which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Economic Incentives
Many regions offer incentives for installing energy-efficient systems like solar hot water heaters. These can include rebates, tax credits, and other financial incentives which can help offset the higher initial costs and encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly technologies.
By considering the economic and environmental impacts of their hot water system choices, consumers can make informed decisions that balance cost, efficiency, longevity, and sustainability. This holistic view not only addresses immediate needs for hot water but also aligns with broader environmental goals and financial planning.
Conclusion
Choosing the right water heater system and maintaining it properly are crucial for maximizing both the hot water system’s lifespan and efficiency. The type of system selected should align with the specific needs of the household or facility, considering factors such as installation costs, expected lifespan, and energy efficiency. Maintenance plays a critical role in extending the longevity of the system, reducing lifetime costs, and ensuring continuous efficiency. Innovations in technology and more widespread adoption of energy-efficient systems like solar and heat pump water heaters are likely to shape the future of domestic hot water systems. Including gas hot water systems, an informed approach to selection and maintenance will not only save money but also contribute to a more sustainable use of resources.